The AI Future of Frontend Development

The world of programming has been evolving at a rapid pace in recent years, and the integration of AI into the development process is one of the most exciting advancements. AI tools such as ChatGPT have made it easier than ever to outsource programming work, and this has significant implications for the future of frontend development. As a result, it's vital to explore how AI is impacting the programming field, specifically frontend engineering.
In a recent episode of my podcast, Working Draft (in German), we delved into the impact of AI on engineering and discussed the future of working in the engineering field with a particular focus on frontend development. During this discussion, I shared my vision of where we might be heading in the coming years. This led me to write this article, where I can expand on some of the ideas that have been floating around in my mind for quite some time.
As we continue to embrace AI tools in programming, there are many questions that we must consider. For example, how will this impact the way we work? Will it change the nature of frontend development? What are the implications of this for businesses, developers, and end-users? How does the job of a frontend developer transform through AI? These are some of the critical questions that we'll explore as we delve into the future of frontend development with AI.
The Sigmoid Curve of AI
In his video titled "I tried using AI. It scared me.", Tom Scott offers his perspective on the potential impact of AI in the coming years. He suggests that we may be at the beginning of a sigmoid curve for AI, which could disrupt industries similarly to how Napster disrupted the music industry in the early 2000s. It made the CD obsolete and made way for music streaming as we know it today. The disruption of AI has the potential to significantly alter the way we work, live, and interact with technology. Maybe it even will make parts of engineering obsolete.
As AI tools become more prevalent, we can expect to see a greater level of automation in engineering. This will include automating tasks such as page creation, component development, and much more. However, it's essential to note that the role of each individual working in the field of engineering will be to act as the gatekeeper of the output of these tools. Engineers will be responsible for utilizing and leveraging these tools to their fullest potential.
With this increased automation, the job of engineers will likely shift towards a more strategic focus, with a greater emphasis on problem-solving and decision-making. As a result, engineers will need to develop new skills to effectively collaborate with AI tools and incorporate them into their workflow to create value even faster. While this change may seem daunting, the potential benefits of working alongside AI tools are vast and could lead to significant advancements in the field of frontend development.
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence and refers to computer systems that can perform human-like tasks such as learning, problem-solving, pattern recognition, decision-making, and language understanding.
The Three Stages of AI
Artificial intelligence as such as been used as a term for a multitude of tools and approaches to work. Generally, AI is broadly divided into three stages:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): The chess program that can win against all human intelligence, think Siri, Alexa - fully available today.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): The AI is capable of performing comparable to a human: conversing fluently, making a coffee, get employed at a job and doing it well. We are not there yet, scientists think we will need a couple of more decades to fully unlock this level, maybe 2070.
- Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI): At this level, an AI will learn from itself and will become more intelligent than human life, think sci-fi - it's in the distant future.
In our Working Draft episode on ChatGPT and AI tooling, Peter, Vanessa and I formed a different set of layers AI tooling is capable of doing:
- Optimizing Input (Recontextualize): This layer involves optimizing input based on the model and requested prompt for a given context. For example, if a user provides a long text, an AI tool could be used to summarize it and extract the key information. Another example is translating a text into another language or turning a list of achievements into a text. This layer is useful for automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing engineers to focus on more complex challenges.
- Reciting Information (Researching): This layer involves reciting information that the model is trained with and putting it into a given context. An example is an excerpt of a historic event and comparing it to another event. In more engineering terms, this layer allows AI tooling to find similar cases from what it has learned and put them into context. For instance, an AI tool could help engineers write Unit Tests based on a given input by finding similar cases that have been tested before. Another example is getting an answer to what the RegEx for parsing an email address is, by searching for similar patterns that the AI model has learned.
- Bringing Together Data (Synthesis): This layer involves bringing together multiple data points and forming something new. For example, generating a music song based on the style of a genre of images - we know how to analyze images for their genres and could potentially build a song, bringing it together today is at least difficult. This layer is particularly useful for generating creative outputs, where AI can help augment human creativity by suggesting new ideas and combinations of ideas. However, this layer is also the most challenging, since it requires a high level of understanding of different data types and how they can be combined effectively.
Now let's see how these three layers can be put into action with frontend development.
From Design to Implementation to the User
A foundation for almost any website or application today is a design system in any form, at least describing a theme and re-usable components. Let's focus on building a design system using AI first.
Starting with a fresh design system, insights and recommendations for optimizing it can be gained by examining existing design systems and their construction.
AI tooling can be utilized to generate a design system by leveraging the synthesis layer to bring together multiple data points and generate an enhanced version. A potential tool could be fed with data on various design elements, such as color schemes, typography, and component interactions, as well as examples of existing design systems. The AI tooling would then use this input to generate a new, cohesive design system that adheres to the specific requirements and constraints provided. We will talk about it below.
A tool can be used to recontextualize the input based on the requested prompt, such as generating variants of a button based on different contexts, and ensuring that the output is tailored to the specific context it's used in.
So AI is a shoo-in to help wield a design system, and to participate in the creation of a design system’s assets. But there are many many many rocks that haven’t been turned over yet.
Building a Design System
Theming
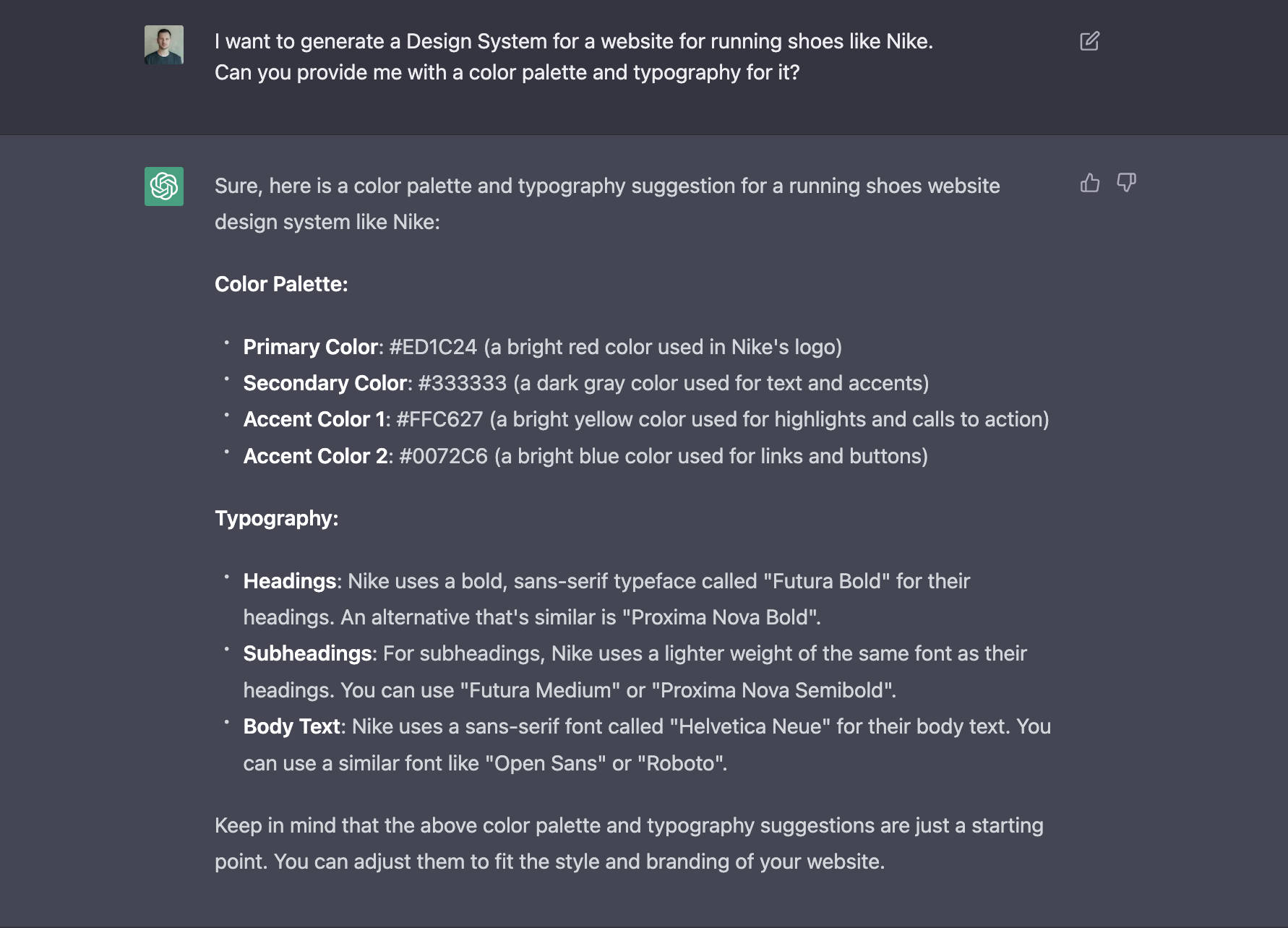
Building a design system isn't complicated. Just ask ChatGPT. Florian tried to generate a Design System using ChatGPT. I tried this simple request to build a design system for a website for running shoes and provide me with the color palette and typography. The output is quite useful.
Components
Taking this as a foundation for a design system, adding some design to create the initial components, or even easier, asking a tool like Midjourney to generate these, isn't a big step.
While I have made it work to generate a decent output for a button component, this is just a matter of experience, crafting the right commands and the machine to get the right data input. Let's assume, in a first step, you train your model on a bunch of existing design systems you can find via Design Systems Repo or similar.
Then you craft the initial component, let's say a button, based on the style input generated by ChatGPT using the tool until you are at the level of what you want. Now you can use this button as an input for your next request, for example a card component. Generating any consecutive component will always match your design style. The AI does the heavy lifting.
The tool Uizard automates the process of generating designs and components from mockups. In his 2021 article, Tony Beltramelli discusses the underlying AI technology that powers Uizard and enables it to transform images into editable designs.
Design to Code
To further streamline the frontend development process, engineers can use tools like Fronty to generate code from their designs. This AI tool can create websites from mockups and code, eliminating the need for engineers to write every line of code by hand.
Once the code is generated, engineers can focus on separating it into manageable components, ensuring that each piece is optimized for performance and meets the specific needs of the project. By using AI to automate the code generation process, engineers can save time and focus on the more complex aspects of development, ultimately resulting in faster and more efficient project delivery.
One example of this efficiency is the possibility to generate code for multiple platforms at once. A tool is capable of providing output as a Swift UI component, as well as for React or another library for the web.
Generating Web Pages
On a web page, you want to display some matching data. New page-types get automatically generated based on the data, we see this with fully auto-generated, personalized experiences done by recommendation engines today. Bringing this to the next level, an AI can generate endless pages with dynamic page types based on the input data you provide, for example user signals (analytics) and your businesses KPIs.
The Role of an Engineer with AI
Here is the gist of it:
- Collaboration: Work with AI
- Judgement: Control AI output
- Critical thinking: Focus on high-level tasks
- Custom solutions: Integrate AI
- Ethical responsibility: Ensure ethical AI use
Let me explain this an in more depth.
As AI continues to become more integrated into frontend development, the role of an engineer will shift towards a focus on collaboration and strategy. Engineers will need to be skilled at working with AI and crafting the right prompts to generate the desired output. However, it's essential to note that the output generated by machines will only be as good as the data it consumed. Therefore, engineers will also play a crucial role in controlling the output of these tools, ensuring that the generated output is tailored to the context it's used in and that it's helpful in achieving the desired outcome. Moreover, as an engineer, your role will move away from knowing specific frontend frameworks to knowing specific Machine Learning tools.
For example, consider the generated components for a design system. Engineers will need to evaluate the necessary variants of a button in a given context that the AI tool needs to generate. They will also need to assess whether the generated variants are useful in the context they are used in, and ensure that the actions triggered by the buttons are properly mapped to the interactions with them. In essence, engineers will act as the critical bridge between AI tools and the final product, leveraging the power of AI while also bringing their expertise and judgement to ensure the optimal outcome.
In addition to collaborating with AI tools and controlling the output generated by them, engineers of the future will likely spend more time focusing on higher-level tasks that require critical thinking and decision-making. With the more mundane and repetitive tasks being automated, engineers will have the opportunity to focus on more complex challenges and use their skills and expertise to solve more significant problems. This will lead to the fact that the role of User Experience Designers and Frontend Engineers will move closer together.
This could include tasks such as designing complex systems, evaluating and selecting the most appropriate tools and technologies to use, and optimizing performance and scalability. Engineers will also need to understand how to integrate AI into these systems, evaluating the potential impact and benefits of different AI tools and techniques, and developing custom solutions to meet specific needs.
Moreover, engineers will play a vital role in ensuring that AI tools are used ethically and responsibly. They will need to be aware of the potential biases that can be introduced by AI tools and work to mitigate them. They will also need to ensure that AI tools are used in ways that align with ethical standards and best practices.
Overall, engineers of the future will need to be highly skilled, versatile, and adaptable, able to work collaboratively with AI tools while also bringing their unique expertise and perspective to the table. By doing so, they will help to drive innovation, enhance productivity, and create more effective and efficient frontend development workflows.
Reasons to Strive for this Future
There are several compelling reasons why striving for a future where AI is more integrated into frontend development could be highly beneficial.
Firstly, it could significantly enhance productivity and efficiency. By automating mundane and repetitive tasks, engineers could focus on more complex challenges and use their skills and expertise to solve more significant problems. This could lead to faster development cycles, shorter time-to-market, and ultimately, a more competitive and innovative industry.
Let's talk about the multi-platform example from above again: Imagine you want to build a design system that can be used across multiple platforms, such as the web, iOS, and Android. Today, this would require writing code multiple times for each platform. However, with AI tooling, these adaptations can be done automatically. By building a design system once in a single language, engineers could export the code and let machines handle the task of transplanting it into several languages for different platforms. This would result in massive time and cost savings, allowing engineers to focus on more complex challenges and innovations.
Secondly, it could help to address the shortage of skilled talent in the frontend development industry. With AI tools doing some of the heavy lifting, engineers could be trained to work more efficiently and effectively, allowing them to take on more complex challenges and develop a broader range of skills.
Thirdly, it could help to reduce the potential for errors and inconsistencies in frontend development. By automating tasks such as generating code and components, AI tools could reduce the likelihood of human error and ensure that development work is consistent and high-quality.
Finally, integrating AI into frontend development could help to drive innovation and improve the user experience. By leveraging AI techniques such as natural language processing and computer vision, engineers could develop more intelligent, responsive, and personalized user interfaces that better meet the needs and preferences of users.
Overall, a future where AI is more integrated into frontend development could bring significant benefits, enhancing productivity, addressing talent shortages, improving quality and consistency, and driving innovation in the industry.
Beyond Frontend Development
In addition to using AI tools like Fronty for design to code automation, there are many other possibilities for using AI in frontend and backend engineering. For example, ChatGPT can be used to automate backend tasks, such as generating system diagrams, optimizing database designs, and creating service meshes. With the help of AI, engineers can quickly and easily generate complex infrastructure diagrams and database designs, saving time and effort in the development process. Additionally, AI can be used to automate tasks like testing and deployment, enabling engineers to focus on higher-level problem-solving and innovation. Just take GitHub Copilot as an example. It "uses the OpenAI Codex to suggest code and entire functions in real-time, right from your editor."
Ask the machine, it will give it to you.
So What does it Mean for the Near Future?
The future of frontend development is exciting and rapidly evolving, with AI technology poised to have a major impact on the industry. As Brad Frost has noted in his aforementioned article "Design Systems in the Time of AI", there are already examples of how AI is automating aspects of the job, such as removing backgrounds from images. As AI technology continues to advance, it's likely that more and more of the frontend engineering process will be automated. This will not only lead to greater efficiency, but also a shift in the skill sets required for frontend developers. As such, developers who stay on top of the latest technology and continue to develop their skills will be best positioned to succeed in the industry.
While it's clear that AI will play a major role in the future of frontend development, there is still much to discover and explore. We can expect to see a variety of new tools and technologies emerge in the coming years, many of which will be built on AI principles. For example, ChatGPT and Midjourney are just two examples of how AI can be used to streamline frontend development processes. As more developers explore the potential of AI and incorporate it into their workflows, we will undoubtedly see a range of new innovations that will continue to shape the industry.
However, it's important to note that the human element of frontend development will never be entirely replaced by machines. While AI can automate many tasks, it cannot replicate the creativity and ingenuity that comes from human designers and developers. As such, it's important for developers to embrace new technology while also staying true to their own unique creative vision.
In conclusion, the future of frontend development is sure to be exciting and full of opportunities for innovation. As is with so many other roles. Let's see how rapid we are pacing towards this exiting future.
If you want to learn more about how ChatGPT works, read this article.
Do you want to discuss the ideas I outlined? Reach out via Twitter. And if you enjoyed my thoughts, consider sharing the article.
Special thanks to David for helping review this article and providing constructive feedback.